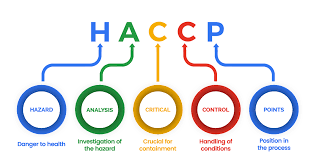
HACCP is standard that has been adopted across the world in food industries and is the foundation for federal food inspection within the United States. The practical prevention based is founded on science. The body focuses on control and prevention of food safety threats which are normally in three categories namely physical, biological and chemical hazards. The program is more inclined to food safety as opposed to food quality thus should not be differentiated from quality assurance supplements. Its objective is to ensure operational hygiene, sanitation as well as other workable considerations to be carried out so as to yield products that are safe and provide evidence that safety practices have been adhered to.
HACCP basically analyses the flow of food via the production process offers a mechanism to regulate and monitor these operations regularly and to ascertain the critical points for foodborne disease hazards control. A hazard is any potential threat that can result in harm to the consumer of a food product. On the other hand, a critical point is a step or process through which control or preventive measures can be enforced that will do away with, minimize or eliminate a hazards that has happened before this point. This system has become indispensable in process control within microbiological hazards. This methodology is a simulation of the trend towards more complex within food inspection and sanitation.
HACCP has been accepted by governments as well as deployed by progressive food industries. The hazard has two main components analysis of hazards and definition of critical points. Analysis of hazards necessitates a comprehensive knowledge on food microbiology as well as microorganisms that might be present and more importantly the aspects that impact on their survival and growth. Food acceptability and safety are most affected by poor temperature control during processing as well as storage, contaminated raw materials or adjuncts, poor cooling from after processing, improper or in-effective cleaning of equipment’s used in the production process, poor hygiene by those involved in the production process, not separating cooked and raw products and finally cross contamination after processing.
The HACCP system evaluation procedure elucidates the product and its target use as well as identifying any possible dangerous food components subject to microbial proliferation and contamination during food preparation or processing. Hazard analysis is a process for carrying out risk analysis for food ingredients and products through diagramming the entire process to showcase the distribution and manufacturing sequence, survival, microbial proliferation and contamination capable of leading to foodborne diseases. Critical control points are established through a flow chart. Any loopholes that are identified are corrected on priority. Monitoring procedures are then created to assess effectiveness.
The HACCP system adopted by food industry companies and monitored by regulatory bodies, provides the companies with tools and a competitive edge as well as protecting the consumers efficiently and effectively. It also provides a comprehensive rational methodology to control of microbial dangerous substances in foods as opposed to conventional inspection techniques. It is currently the trend in food processing but has an opportunity of evolving into a more comprehensive program for maximum quality management in times to come. Consumers duly expect that the food products that they purchase is safe for consumption. Contaminated food products can obviously lead to foodborne diseases which makes patients uncomfortable or in some cases lead to death. Food safety is intrinsically connected to chemical, physical or biological hazards which may happen unpredictably within the food chain right from the farm to the point when it is consumed thus making HACCP the most relevant and up to date standard to guarantee consumer safety.
Impact of HACCP in the Food Industry
The HACCP system has been acknowledged globally as a food safety assurance standard. Mandatory or recommended use of the system is entrenched in laws of many countries, industries and it is being accepted by consumers widely. Below are scenario of relevant cases where HACCP has been adopted in the food industry.
In Sau Paulo Brazil, the Health Ministry in 1994 made the HACCP system mandatory for all facilities dealing with food handling through Portaria 1428. The agriculture Ministry in 1998 ascertained the application of the system in industries dealing with animal origin products through Portaria 46. The United States of America Food and Drug administration in 1972 determined the use of the HACCP system for canned foods of low acidity. Currently the body as well as agriculture ministry necessitate the application of HACCP for beef, fish and poultry products. In 2001, the FDA necessitated that both domestic and international producers of fruit juice adopt HACCP in their production processes. The same was also adopted for industries dealing with exportation of wine.
Across Europe, food industries are legally obliged for the safety of the food products they produce, sale or transport. They are required to implement a preventive methodology by finding out and controlling dangers before food safety is compromised. To fulfill this requirements, most food industries now depend on industry standards such as HACCP. Within the European Union, the HACCP system is entrenched in the council directive number 94/43 on food products hygiene. This council directive was inculcated on 2000 on the food safety whitepaper and has been revisited regularly and amended with more regulations.
The Canadian government in conjunction with its fishing industry established a quality management program in 1993 deemed the first mandatory inspection program globally that was founded on HACCP. Canada is striving towards the deployment of a food safety improvement agricultural program which stimulates HACCP adoption since it fosters food safety. In some nations where HACCP has not been made mandatory, seminars for health inspectors is founded on this system. Some justifications for widespread adoption by the food industry are reactions to legal requirements, expectation of future requirements, attention in export markets as well as the need to reduce production costs and improve food safety.
Within the past 5 years, most Asian nations including Malaysia have adopted national HACCP system programmes for their fish processing zones in conjunction with global trends. Good manufacturing practices as well as HACCP are predominant food safety standards being implemented by the Malaysian food industry. However, good manufacturing practices is only applied as a pre-requisite to HACCP system.
Impact of HACCP on Food Safety
Within the past years, the pursuit for food safety has been marred by critical developments in food production like reduced periods between production and product consumption, innovations and use of technology in the manufacturing processes, improved prevalence of a few microorganisms and improved shelf life of products. Since the food chain has become international, food security is now perceived from a different viewpoint and now represents one of the biggest health concerns globally, impacting on the lives of millions of people annually as well as contributing to substantial social and economic consequences.
Regardless of the technological advancements in food control and production, the occurrence of foodborne related diseases has increased recently even in countries that are considered developed. Food contamination and hazards might result from initial production, handling of food products in the farm, poor storage and transportation to the food industries or simple mistakes during processing in hotels or homes. Though at the moment it is not considered as a serious issue, food safety has become an increasingly vital aspect, both in magnitude and with regard of health consequences for the overall population. Concepts connected to demographic situations, supply chain, health infrastructure, lifestyle and environmental aspects of each country contribute to the increased frequency, prevalence and consequences of these ailments.
Considering all the above factors, HACCP remains a critical tool in management of quality within the food industry today, bringing product integrity and protecting consumer’s health. Implementing a HACCP system should now be mandatory since it makes sense and good science. For food industries, it is absurd to invest many resources in purchasing and processing food products only to have them recalled later due to pure standards and losing all the profits. HACCP should be entrenched into sanitation pans to create a maximum food safety program from inception to the consumer through including plan sanitation and cleaning policies. Currently, standards in the food industry play a vital role in assisting food industries to obtain compliance with regulations and in most cases exceed its expectations. More importantly, they allow food industries to ensure consistency with regard to product quality and safety.
How HCCAP related to the sea food plant
The current see food industry faces so many challenges, with more sophisticated products and processes demanding rigorous controls in the storage, processing and distribution to various end points. The idea of HACCP does guarantee the safety of see food products, promoting the confidence of consumers in the sea food industry, while equally motivating export growth in third world countries to create a stable food safety control system. In the sea food industry HACCP implementation is at different levels globally in a bid to better and guarantee food safety.
The application of HACCP policy in seafood industry has been investigated since 1970. Two bodies namely the National seafood inspection laboratory and the National marine fisheries services in 1986 investigated the possible risks of food products extracted from the sea, this was ignited by an official request from the United States congress. The national marine fisheries service concluded its scrutiny on HACCP implementation within the fishing industry in 1991 under the seafood surveillance project model framework.
A basis for the drafting of fresh inspection systems such the HACCP was awarded by the covenant on Phyto-sanitary and sanitary measures and demands that member organizations adopt measures founded on the risks assessment with the support of scientific evidence. Covenants agreed upon regarding global fish trade also factor in the Uruguay round covenant of 1994 as well as the technical hindrances to trade agreement, though inspection is governed by the Codex Alimentarius. Towards the end of 1986 the fisheries industries division also agreed to adopt the HACCP methodology to the quality assessment of fish.
At the moment, HACCP system is being deployed across the fish industry globally as 1st world nations such as the United States help 2nd world and 3rd world nations in fully implementing it. The government of Canada has already inculcated HACCP within its program on food quality management. For the Ueropean Union, HACCP also focuses on the checks within industries and refer to fundamental principles of domestic auditing.
Use of HACCP in Meat Plants
Federal regulations legislated between 1998 and 2000, demand that all huge, middle size and small scale meat and poultry products processing companies to fully implement an HACCP system plan. For middle size and small scale processing industries, sorting of all the various HACCP information can seem like such a tough task, particularly when resources and time are scarce.
Alarms with regard to the meat industry have a reasonable basis. Meat is a critical agent in food borne infections. Research in an Irish beef abattoir indicate that 3.2 percent of the carcasses had Escherichia contamination while the respective results for Listeria and Salmonella were sixteen percent and two percent respectively. Pork meat is also another critical area with food borne pathogens.
It is universally accepted that HACCP system is the most appropriate methodology in ensuring food security, thus safeguarding the health of consumers. Concerns regarding food security ignited the EC agreement of 2001 which mandates legally HACCP within all poultry and meat industries within the European Union. Pork, Lamb and beef products contribute hugely to economies annually. In the wake of food and mouth disease and Escherichia, the implementation of HACCP system in the dairy industry is thus the best way of avoiding more adverse publicity as well as restoring the confidence of consumers both domestically and globally.
HCCP in relation to Dairy Plants
Many dairy products bear a great record in terms of food safety, because of the well regulated processing conditions. The major possible hazards are microbiological in nature. Pasteurization though, has proved to be fruitful with regard to a CPP to regulate the control classical zones together with fresh foodborne pathogens. Hazards of chemical nature are rarely critical and have in many scenarios been addressed by raw materials suppliers hence reducing the workload of the processing plants. Physical hazards are some correlation mainly during the packaging of dairy products. The dairy industry utilizes several technologies in drying, heating, freezing, curing, chilling and fermenting, hence the HACCP ideology can be fruitfully adopted to every stage of the production process.
The world health organization documentation is applied as a foundation for some opinions particular to the dairy plant. HACCP certification of dairy industries is applicable for substances processed or made through fresh milk or dairy products as the chief raw material such as sterilized milk, formula milk, yoghurt or pasteurized milk; milk power either sweetened whole milk powder, skimmed dried milk powder, whole milk powder as well as infant formula milk, flavored milk powder as well as other types of formula milk powder other substances include milk fat, cheese, lactose, casein and whey powder.
Dairy substances are critical components within the human diet, though several micro-organisms contaminating agents such as veterinary drugs, water and equipment, poor personnel hygiene, chemical toxins and pollutants could also serve as causative agents for several food borne ailments. The systematic methodology to reducing food poisoning incidents and economic loses from all processing procedures in the dairy industry has been greatly influenced by the implementation of HACCP systems as well as standards devised by the international standards organization.
The Codex Alimentarius commission has standardized HACCP system and normally, it is a preventive methodology which maintains, identifies, evaluates, regulates and monitors every production procedure that is critical to food security. HACCP system has seven principle rules namely carrying out a hazard evaluation, identifying the main crucial process points, creating critical limits, requirements for CCP measurement, corrective procedures justification together with documentation procedures and system record keeping. As per the HACCP system, the term hazard means anything or food condition which can possibly cause dangerous health effects.
In dairy industries, these hazards can be physical, biological or chemical emanating from semi processed, processed materials or raw materials. Hazard analysis is the assessment of hazard severity degree as well as its possibility to happen. The multiplication and survival of micro-organisms of concern as well as the conditions causing their persistence of presence in food components thus have to be evaluated. Within this industry, the use of HACCP together with the parallel application of quality management systems and standard operations of procedure like good hygiene practices and good management practices has made it more effective.
The international standards organization introduced the food safety management systems as well as its elements are interchangeably used to create objectives and policy so as to control and direct dairy industries with regard to products safety. Programs based on HACCP have been largely deployed within the dairy industry for yoghurt, condensed milk, ice cream, butter and cheese. The HACCP system has introduced a platform for competition within the dairy industry making industries rush to implement it and leading customers to secure products in industries that have implemented it. Normally, the dairy industry is so challenging since it comprises of several products before a product is sold to the consumer. The many processes make it more sophisticated in ensuring sanitation across hence making HACCP system a critical system for the sector.
What is the Impact of HACCP in the Food Industry?
HACCP remains a critical tool in management of quality within the food industry today, bringing product integrity and protecting consumer’s health.
How can HACCP be applied to Meat Plants?
In the wake of food and mouth disease and Escherichia, the implementation of HACCP system in the dairy industry is thus the best way of avoiding more adverse publicity as well as restoring the confidence of consumers both domestically and globally.